Editor’s Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope was specially designed to detect the faint infrared light from very distant galaxies and give astronomers a glimpse at the early universe. The nature of galaxies during this early period of our universe is not well known nor understood. But with the help of gravitational lensing by a cluster of galaxies in the foreground, faint background galaxies can be magnified and also appear multiple times in different parts of the image.
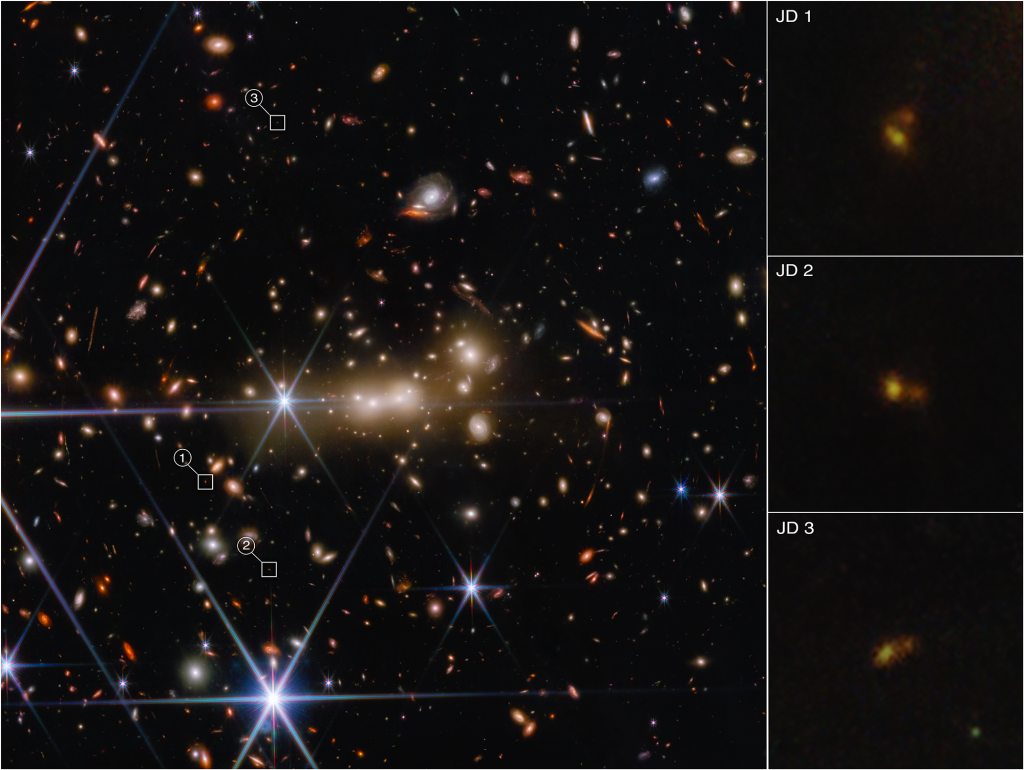
Today, we sit down with three astronomers working on Webb to talk about their latest findings. The team members are Dan Coe of AURA/STScI for the European Space Agency and the Johns Hopkins University; Tiger Hsiao of the Johns Hopkins University; and Rebecca Larson of the University of Texas at Austin. These scientists have been observing the distant galaxy MACS0647-JD with Webb, and they’ve found something interesting.
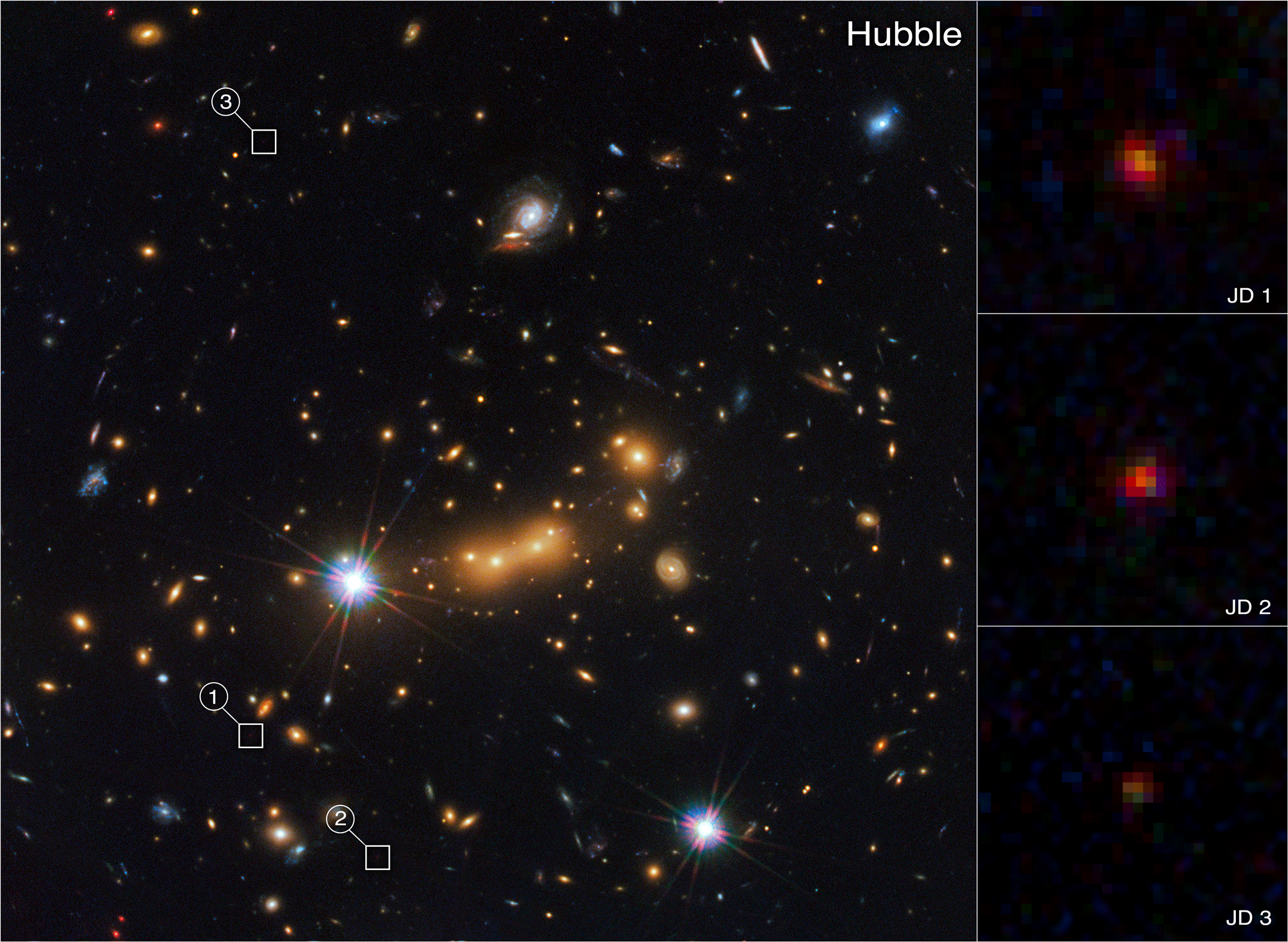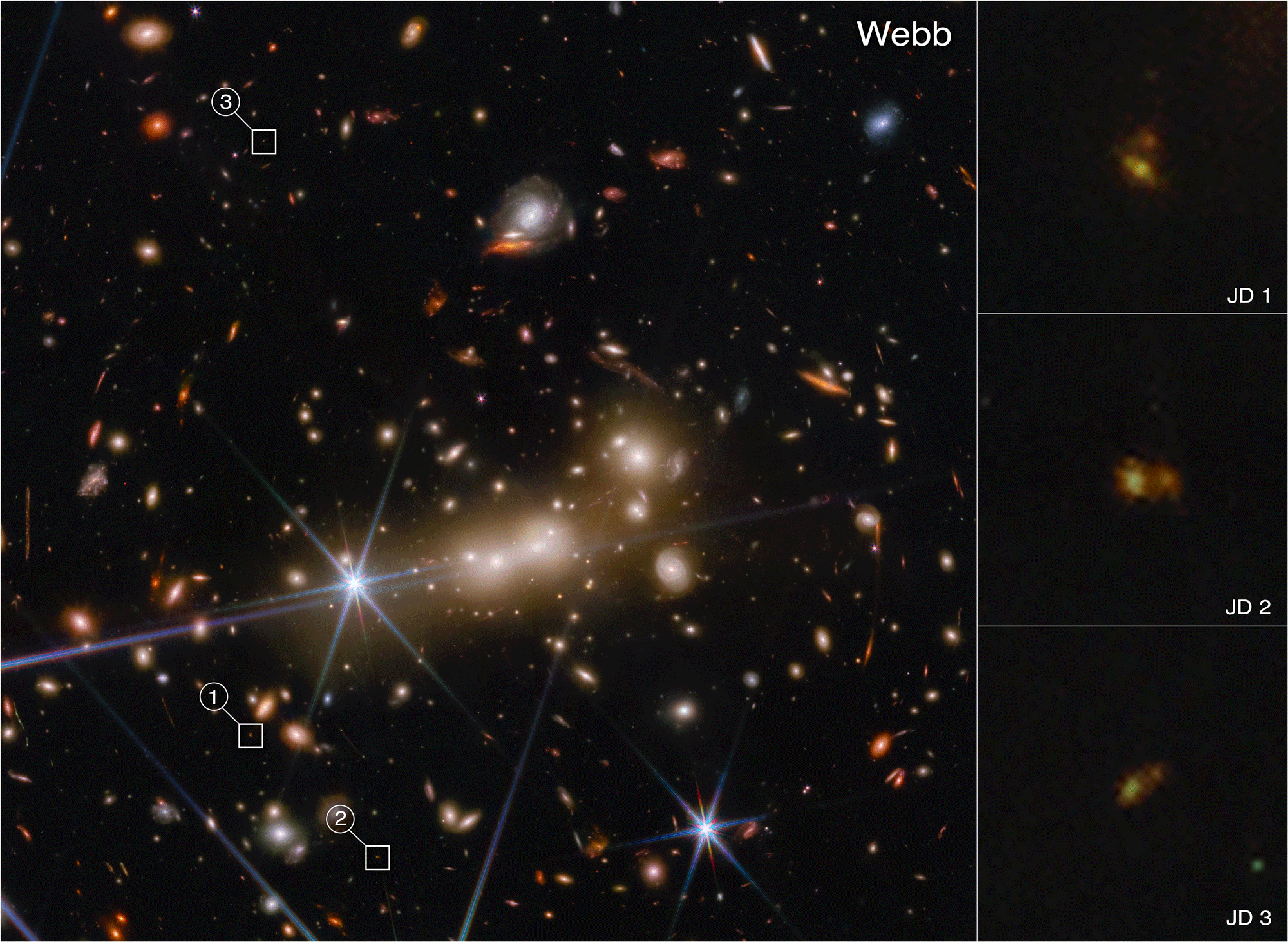
Dan Coe: I discovered this galaxy MACS0647-JD 10 years ago with the Hubble Space Telescope. At the time, I’d never worked on high redshift galaxies, and then I found this one that was potentially the most distant at redshift 11, about 97 percent of the way back to the big bang. With Hubble, it was just this pale, red dot. We could tell it was really small, just a tiny galaxy in the first 400 million years of the universe. Now we look with Webb, and we’re able to resolve TWO objects! We’re actively discussing whether these are two galaxies or two clumps of stars within a galaxy. We don’t know, but these are the questions that Webb is designed to help us answer.
Tiger Yu-Yang Hsiao: You can also see that the colors between the two objects are so different. One’s bluer; the other one is redder. The blue gas and the red gas have different characteristics. The blue one actually has very young star formation and almost no dust, but the small, red object has more dust inside, and is older. And their stellar masses are also probably different.
It’s really interesting that we see two structures in such a small system. We might be witnessing a galaxy merger in the very early universe. If this is the most distant merger, I will be really ecstatic!
Dan Coe: Due to the gravitational lensing of the massive galaxy cluster MACS0647, it’s lensed into three images: JD1, JD2, and JD3. They’re magnified by factors of eight, five, and two, respectively.
Rebecca Larson: Up to this point, we haven’t really been able to study galaxies in the early universe in great detail. We had only tens of them prior to Webb. Studying them can help us understand how they evolved into the ones like the galaxy we live in today. And also, how the universe evolved throughout time.
I think my favorite part is, for so many new Webb image we get, if you look in the background, there are all these little dots—and those are all galaxies! Every single one of them. It’s amazing the amount of information that we’re getting that we just weren’t able to see before. And this is not a deep field. This is not a long exposure. We haven’t even really tried to use this telescope to look at one spot for a long time. This is just the beginning!
About the authors:
Dan Coe is an astronomer of AURA/STScI for the European Space Agency and the Johns Hopkins University. Tiger Hsiao is a Ph.D. graduate student at the Johns Hopkins University. Rebecca Larson is a National Science Foundation fellow and Ph.D. graduate student at the University of Texas at Austin. These NIRCam observations of MAC0647-JD are part of the team’s Cycle 1 program GO 1433 (PI Coe). The team is planning more a detailed study of the physical properties of MACS0647-JD with Webb spectroscopy in January 2023. Read the team’s science paper here.
– Ann Jenkins, Principal Science Writer, Office of Public Outreach, Space Telescope Science Institute
